flowchart LR A(IRA) --> B(Subsidies) B --> C(Investment) B --> D(Jobs) C <--> D C --> E(Domestic Manufacturing) D --> E(Domestic Manufacturing)
Lecture 3 Logic and Causal Models
March 23, 2024
Recap lecture 2
- Types and applications of evaluation
- Exploratory evaluation
- High Line Park
- Cultural responsive evaluation
- Northwest Housing Alternatives
Today’s agenda
- Theory of change
- Logic model
- DAG: Directed Acyclic Graphs
- Causal models
- Jobs Plus in NYC case
- Ask a good question game
Theory of change
Elements of a program
Inputs:
Things that go into an activity; money, people, time, etc.
Activities:
Actions that convert inputs to outputs; things that the program does
Outputs:
Tangible goods and services produced by activities; you have control over these
Outcomes:
What happens when the target population uses the outputs; you don’t have control over these
Inputs → Activities → Outputs → Outcomes → Final outcomes
Source: Gertler et al. (2016)
Capturing the wedege
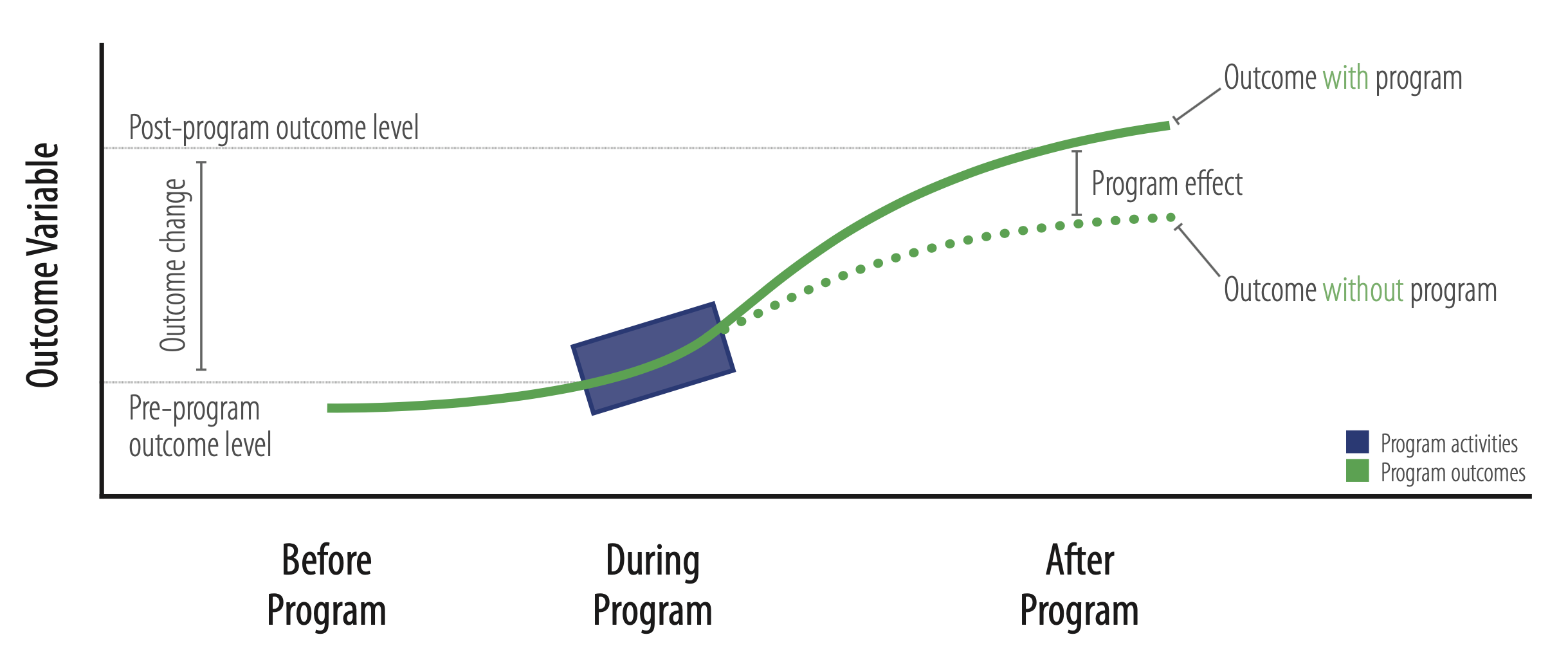
Source: Andrew Wheiss
Data
- Experimental: you have control over which units receive treatment
- Observational: you do not have control over which units receive treatment
Natural experiments
Real experiments could be
- High costs
- Infeasible
- Unethical
Stories
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG)
Directed: Each node has an arrow that points to another node
Acyclic: You can’t cycle back to a node (and arrows only have one direction)
Graph: It’s a graph
Source: Andrew Wheiss
Draw a DAG
Step 1: List variables
Step 2: Simplify
Step 3: Connect arrows
Step 4: Use logic and math to determine which nodes and arrows to measure
What is the causal effect of an additional year of education on earnings?

Source: Andrew Wheiss
Causal identification
A causal effect is identified if the association between treatment and outcome is propertly stripped and isolated.
- Arrows in a DAG transmit associations
- We can redirect and control those paths by “adjusting” or “conditioning”
Three types of associations
Confounding: Common cause

Causation: Mediation

Collision: Endogeneity/Selection

Source: Andrew Wheiss
Confounding example
What’s the relations between money and win margin?

Money \(\rightarrow\) Win
Money \(\leftarrow\) Quality \(\rightarrow\) Win
Quality is a backdoor
Solution:
Find the part of campaign money that is explained by quality, remove it. This is the residual part of money.
Find the part of win margin that is explained by quality, remove it. This is the residual part of win margin.
Find the relationship between the residual part of money and residual part of win margin. This is the causal effect.
Causasion example

Should you control job connections?
- Avoid overcontrolling
Source: Andrew Wheiss
Colliders example

Do programming skills reduce social skills?
Hired by a tech company inadvertently connected the two.
Source: Andrew Wheiss
Colliders example

Height is unrelated to basketball skill among NBA players
Colliders can create fake causal effects
Colliders can hide real causal effects
Source: Andrew Wheiss
Counterfacture, intervention, and effects

- Control backdoors
- Average treatment effect
- Sub groups (age, race, ethnicity, income, etc.)
Causal models
- Instrumental variables
- Randomized controlled trail (RCT)
- Regressional discontinuity (RD)
- Diference in difference (DiD)
- Matching