Lecture 4 Climate Impacts
Gang He
September 7, 2023
A five points “climate haiku”
- It’s warming
- It’s us
- We’re sure
- It’s bad
- We can fix it
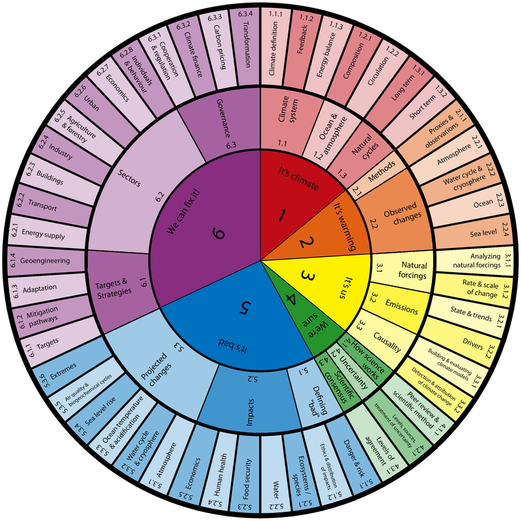
Source: Kimberly A Nicholas
Adverse impacts of climate change
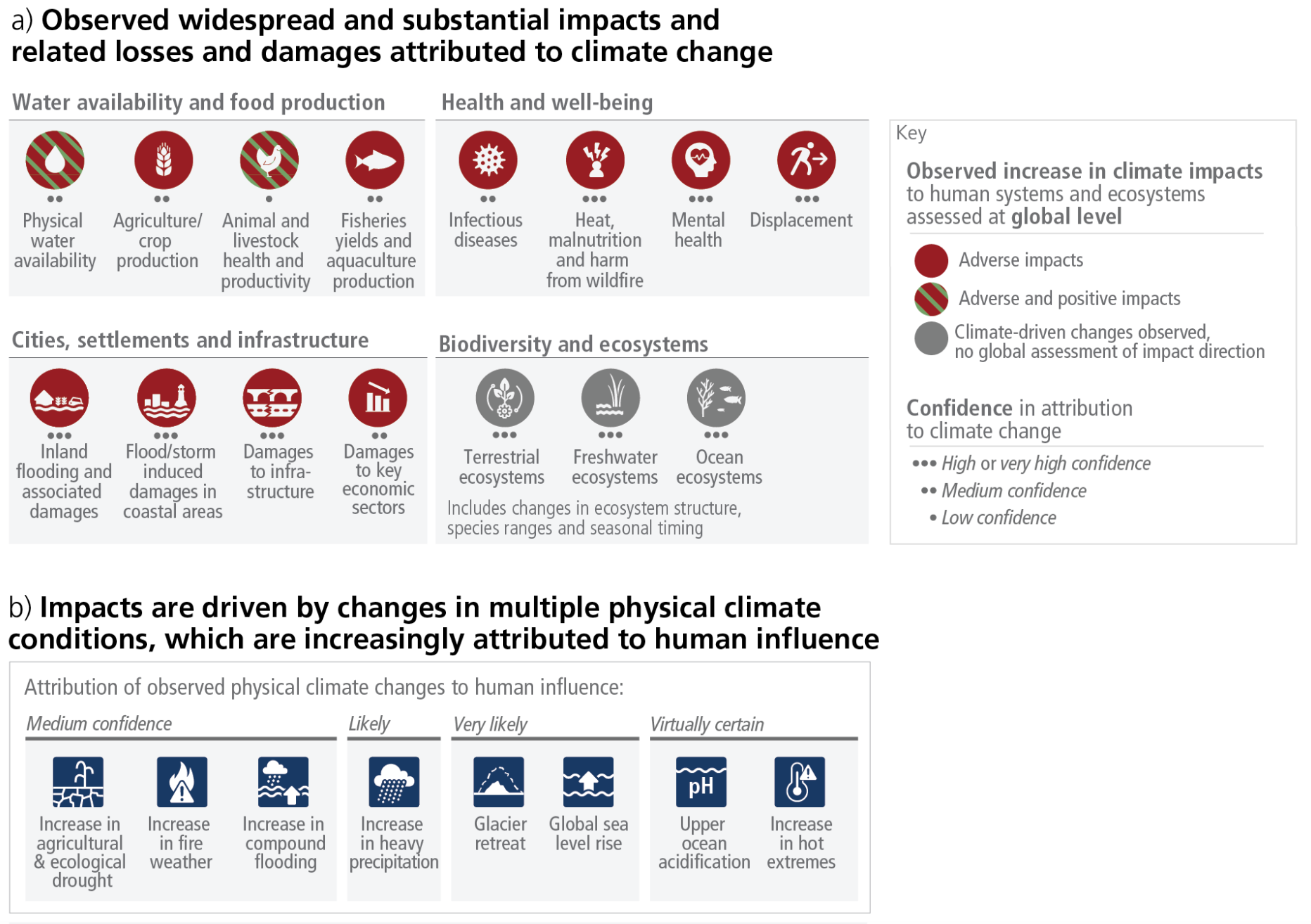
Source: IPCC AR6 Synthesis Repoort Figure 1
The impacts are global
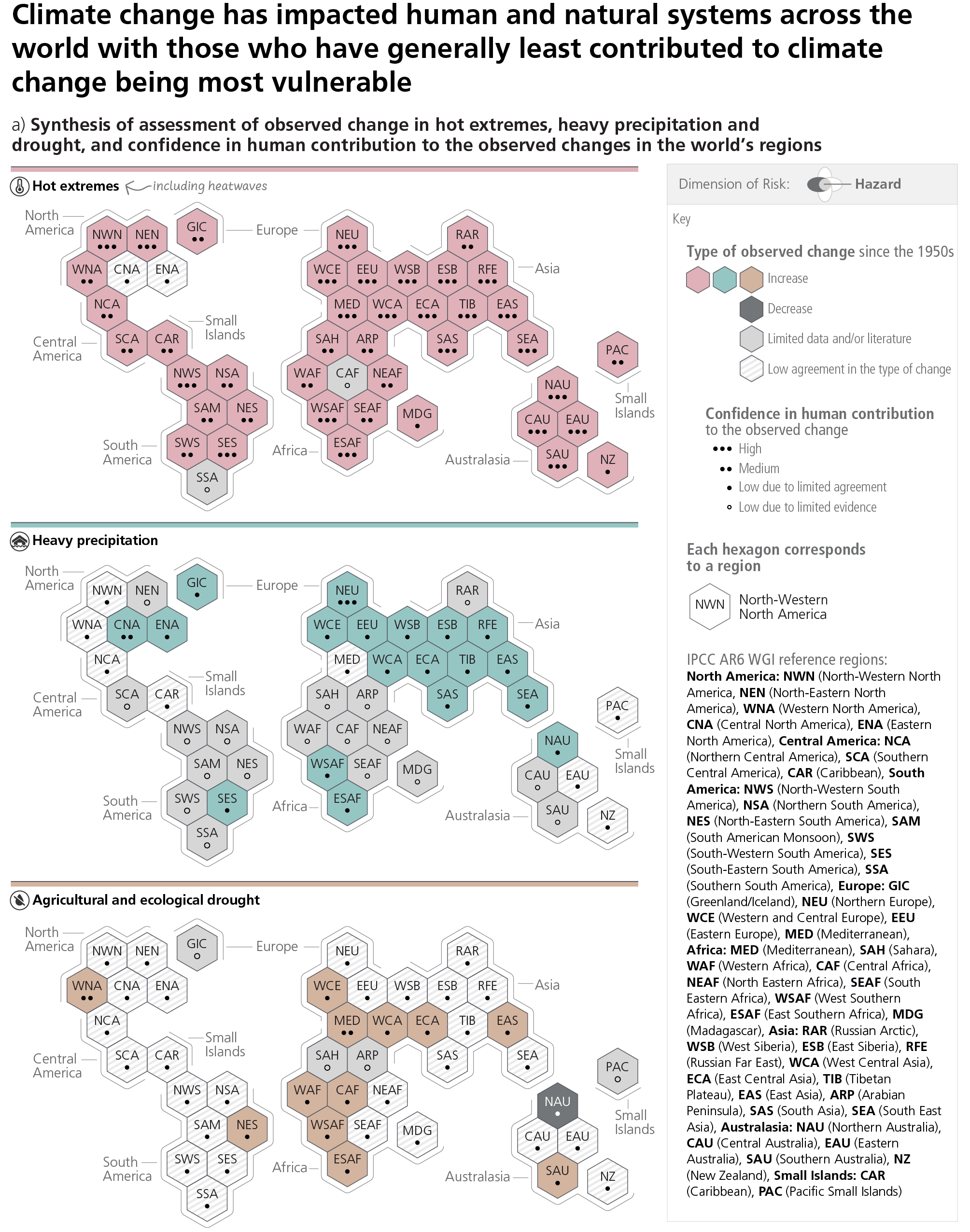
Source: IPCC AR6 Synthesis Repoort Figure 2.3.1
Vulnerable population suffers more
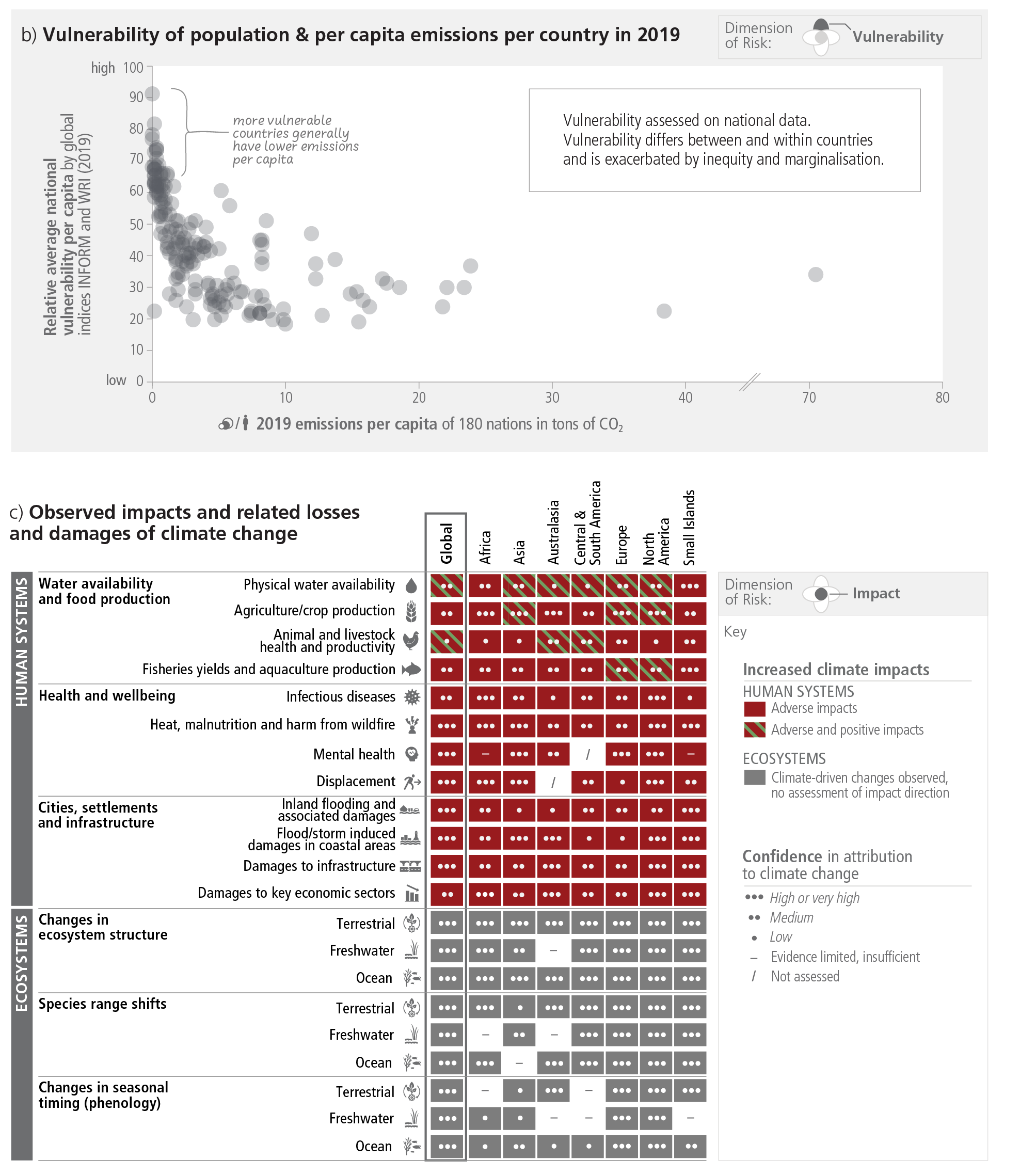
Source: IPCC AR6 Synthesis Repoort Figure 2.3.2
Conventional focues
- Ice melting
- Sea level rising
- Extreme weathers
- Floods
- Droughts
Damages to include
- agriculture
- mortality
- energy
- low-risk labor
- high-risk labor
- coastal damages
- property crime
- violent crime
What other damages to include?
Social cost of carbon
- Marginal cost of carbon
- Cost included:
- Net agricultural productivity
- Human health
- Property damage
- Energy system costs
- Net agricultural productivity
- Cost not included:
- Unknown impact: physical, ecological, economic
- Unknown cost: information
- Unknown impact: physical, ecological, economic
U.S. southern states suffer more
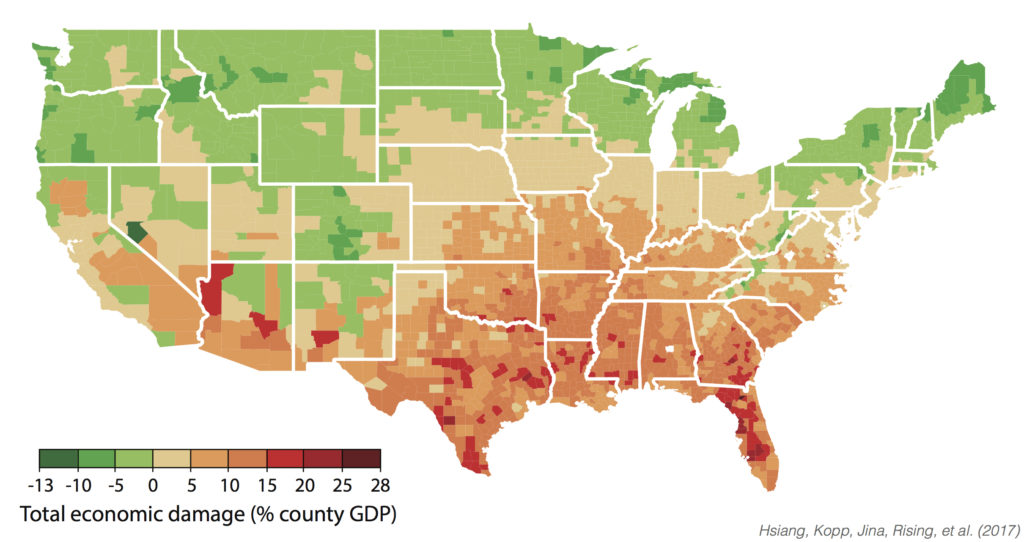
Source: S. Hsiang et al. (2017)
The poor will get damages more
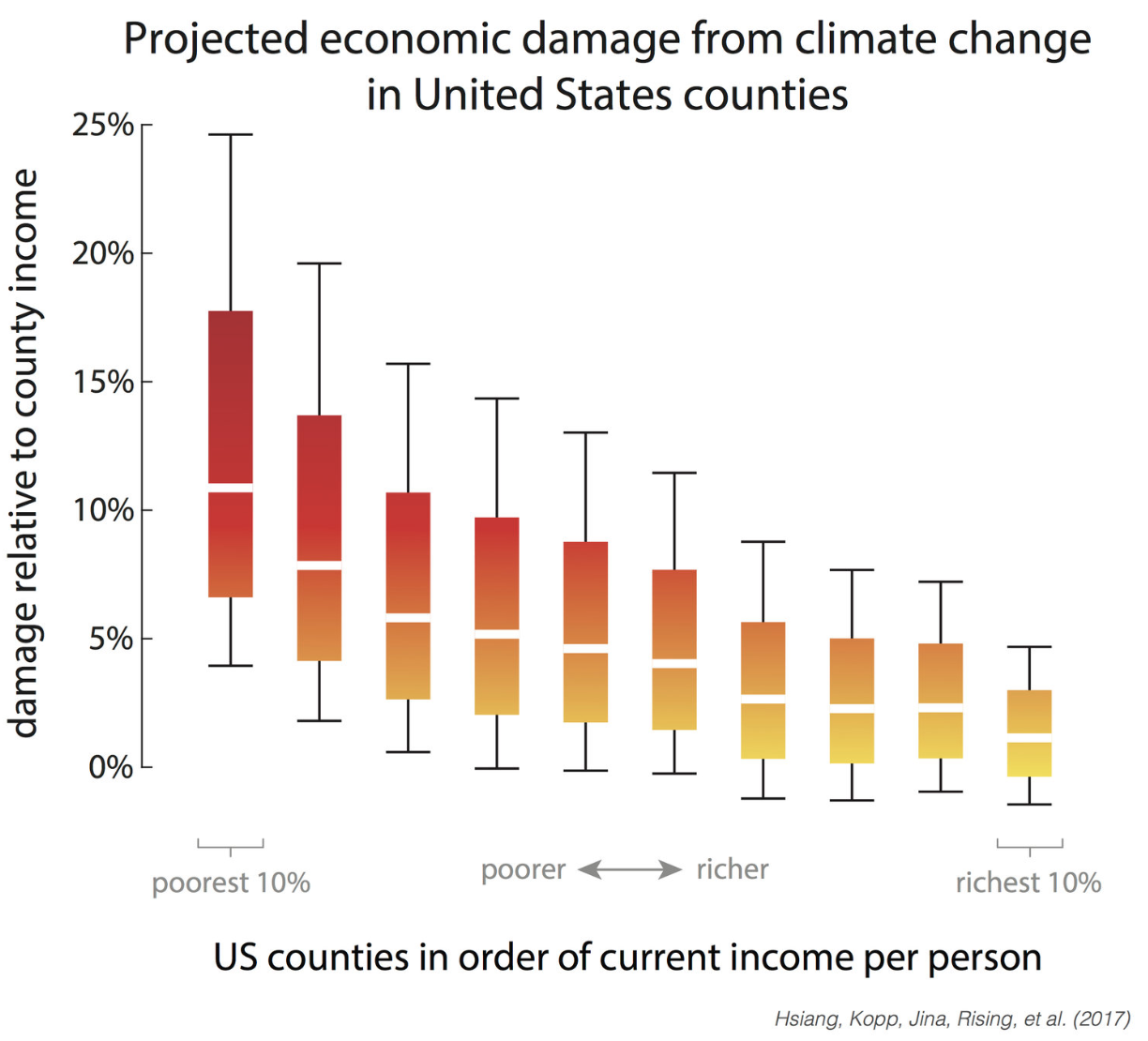
Source: S. Hsiang et al. (2017)
Climate damage function
\(Economic\ Damage=f(\Delta temperature)\)
- It could be negative or positive
- Integrated Assessment Models/Economic models
- DICE/RICE
- FUND
- PAGE
Climate change and conflicts
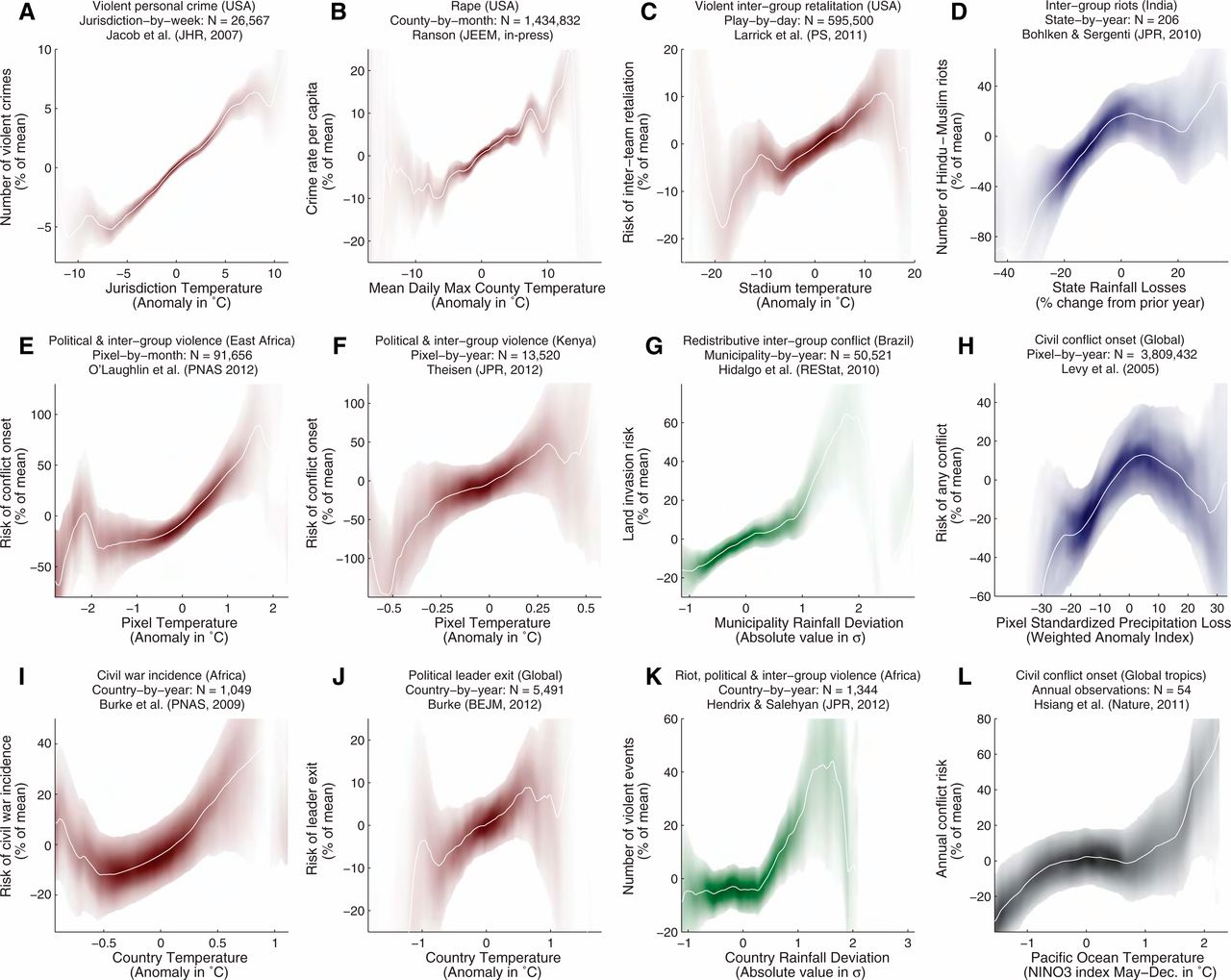
Read more: S. M. Hsiang, Burke, and Miguel (2013)
Climate change affects energy system
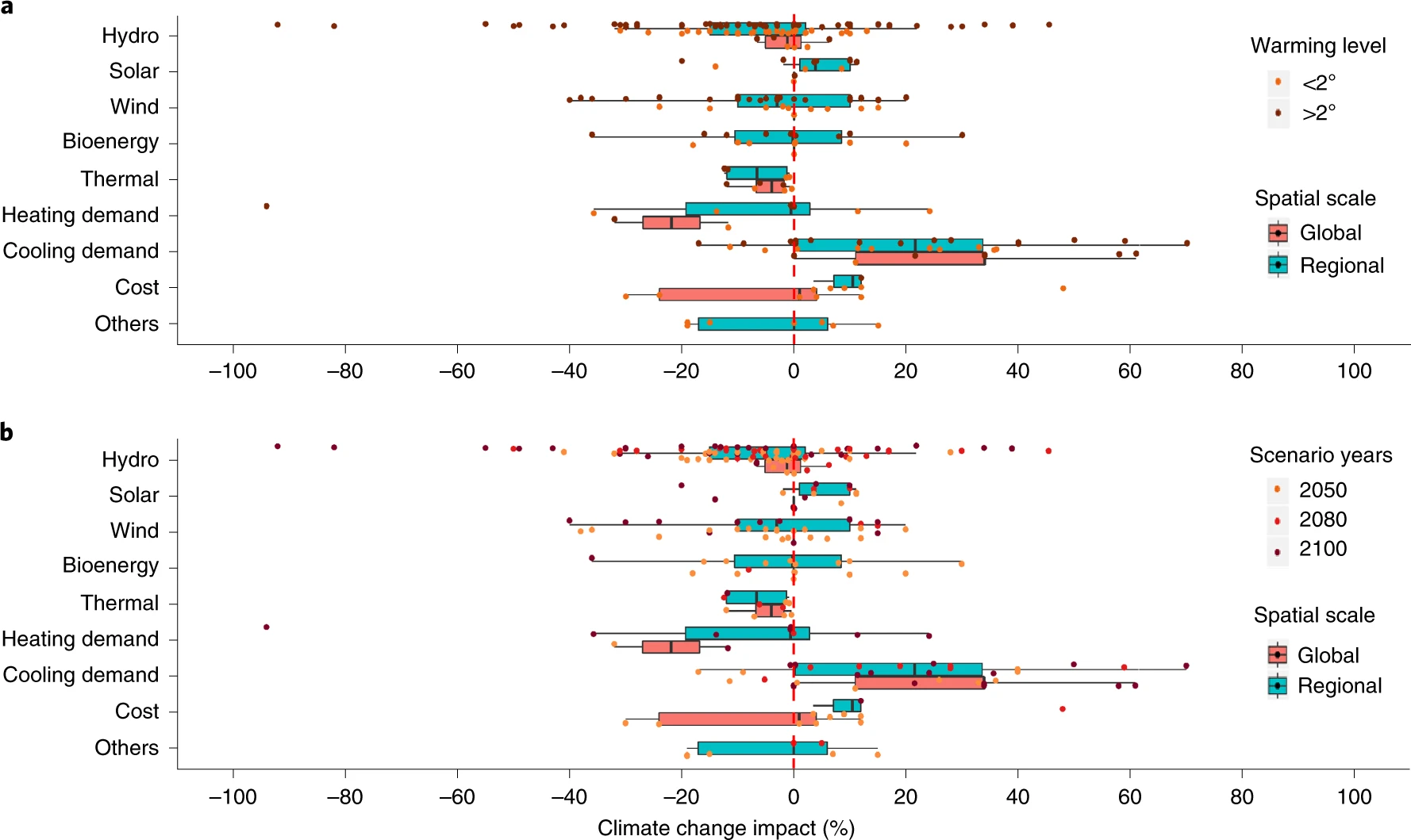
Source: Yalew et al. (2020)
Climate impact to renewable supply-demand match
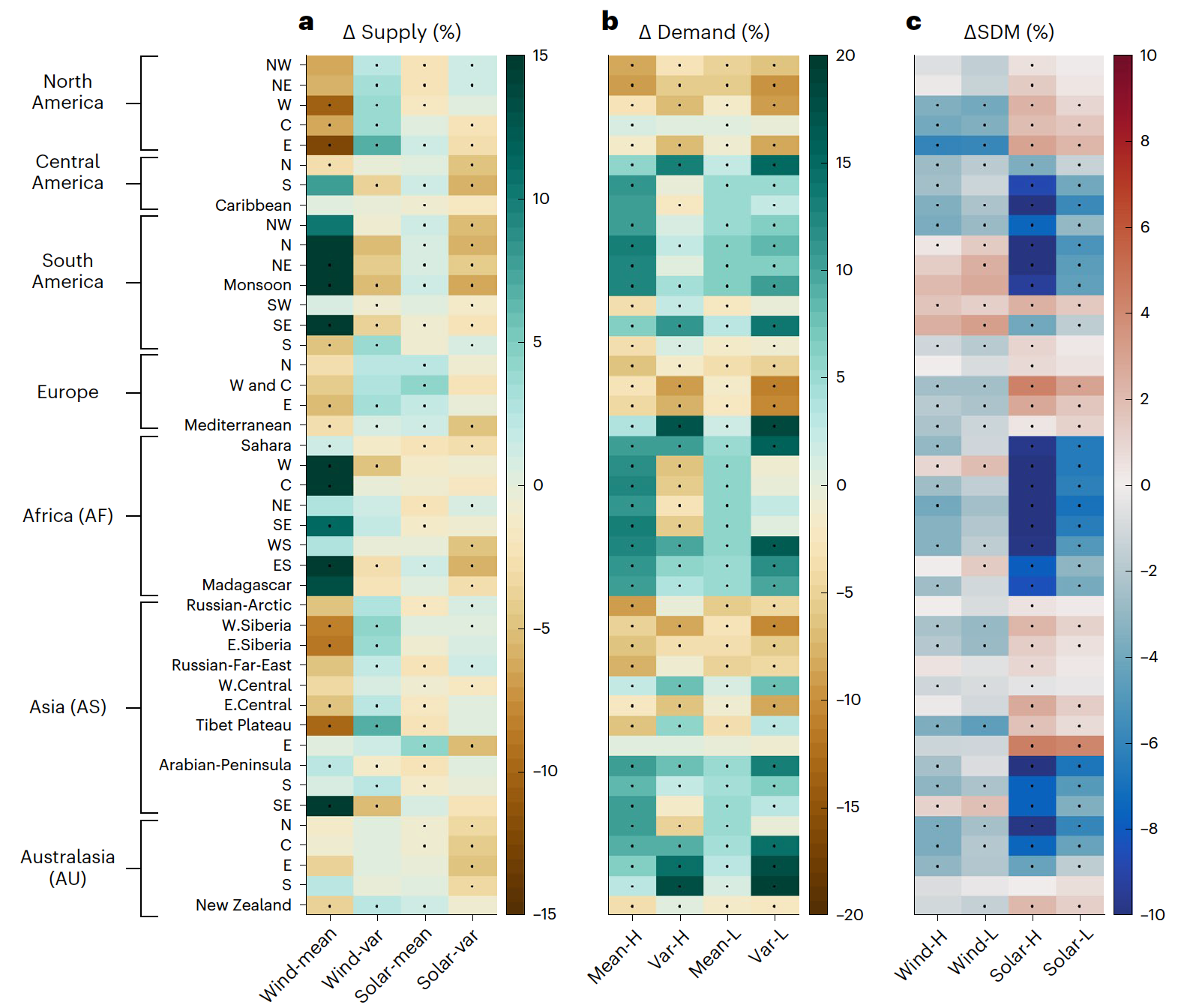
Source: Liu et al. (2023)
NYS climate impacts assessment
- Up-to-date projections of future climate conditions in New York State
- Sector-based literature reviews
- In-depth economic impact assessments
- A peer-reviewed technical report that conveys scientific findings
- Summaries and syntheses for a wider audience
- Adaptation strategies and case studies
- Links and references to primary sources for full transparency

An ongoing effort, anything missing?
Source: New York State Climate Impacts Assessment
Fuel for thoughts: grand challenges, huge progress, and grand opportunities
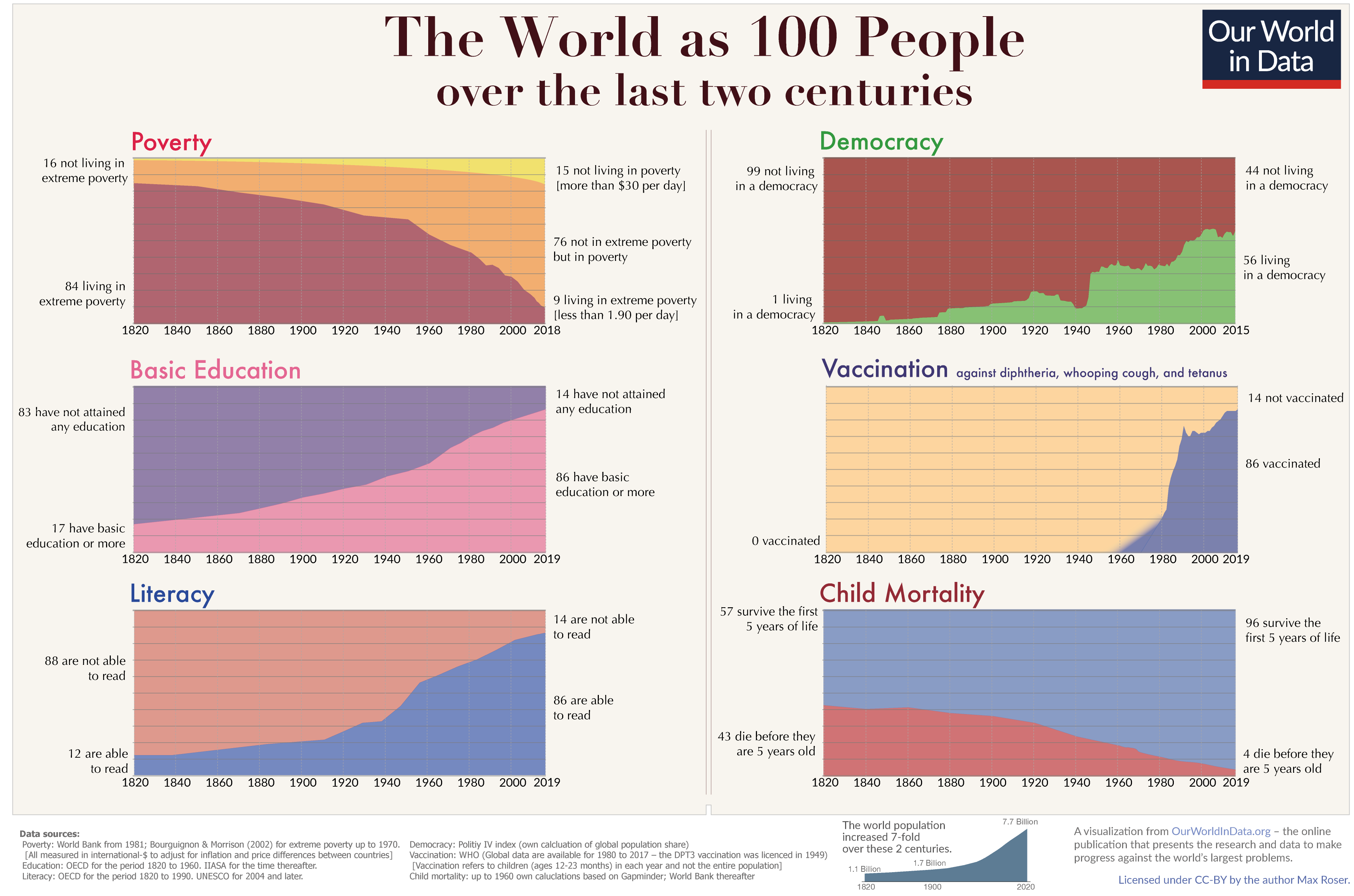
Source: Our World in Data
References
Carleton, Tamma A, and Solomon M Hsiang. 2016. “Social and Economic Impacts of Climate.” Science 353 (6304): aad9837. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad9837.
Hsiang, Solomon M., Marshall Burke, and Edward Miguel. 2013. “Quantifying the Influence of Climate on Human Conflict.” Science, August. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1235367.
Hsiang, Solomon, Robert Kopp, Amir Jina, James Rising, Michael Delgado, Shashank Mohan, D. J. Rasmussen, et al. 2017. “Estimating Economic Damage from Climate Change in the United States.” Science 356 (6345): 1362–69. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal4369.
Liu, Laibao, Gang He, Mengxi Wu, Gang Liu, Haoran Zhang, Ying Chen, Jiashu Shen, and Shuangcheng Li. 2023. “Climate Change Impacts on Planned Supply–Demand Match in Global Wind and Solar Energy Systems.” Nature Energy 8 (8): 870–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-023-01304-w.
Neumann, James E., Jacqueline Willwerth, Jeremy Martinich, James McFarland, Marcus C. Sarofim, and Gary Yohe. 2020. “Climate Damage Functions for Estimating the Economic Impacts of Climate Change in the United States.” Review of Environmental Economics and Policy 14 (1): 25–43. https://doi.org/10.1093/reep/rez021.
Valuing Climate Changes: Updating Estimation of the Social Cost of Carbon Dioxide. 2017. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/24651.
Yalew, Seleshi G, Michelle TH van Vliet, David EHJ Gernaat, Fulco Ludwig, Ariel Miara, Chan Park, Edward Byers, et al. 2020. “Impacts of Climate Change on Energy Systems in Global and Regional Scenarios.” Nature Energy 5 (10): 794–802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-020-0664-z.
Social economic impacts
Source: Carleton and Hsiang (2016)