Lecture 5 Energy Sources and Technologies
September 19, 2022
Sample analytic questions
- How many solar/wind capacities are needed to meet global energy need?
- How much coal can be saved/emissions can be mitigated if China’s average coal power efficiency increased by 1 percentage point?
- Why combined heat and power saves energy?
- How to design the layout of solar/wind farms to improve production?
Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamic efficiency
- Comparing different technologies
- Thermodynamics provides physic limits
Heat engine
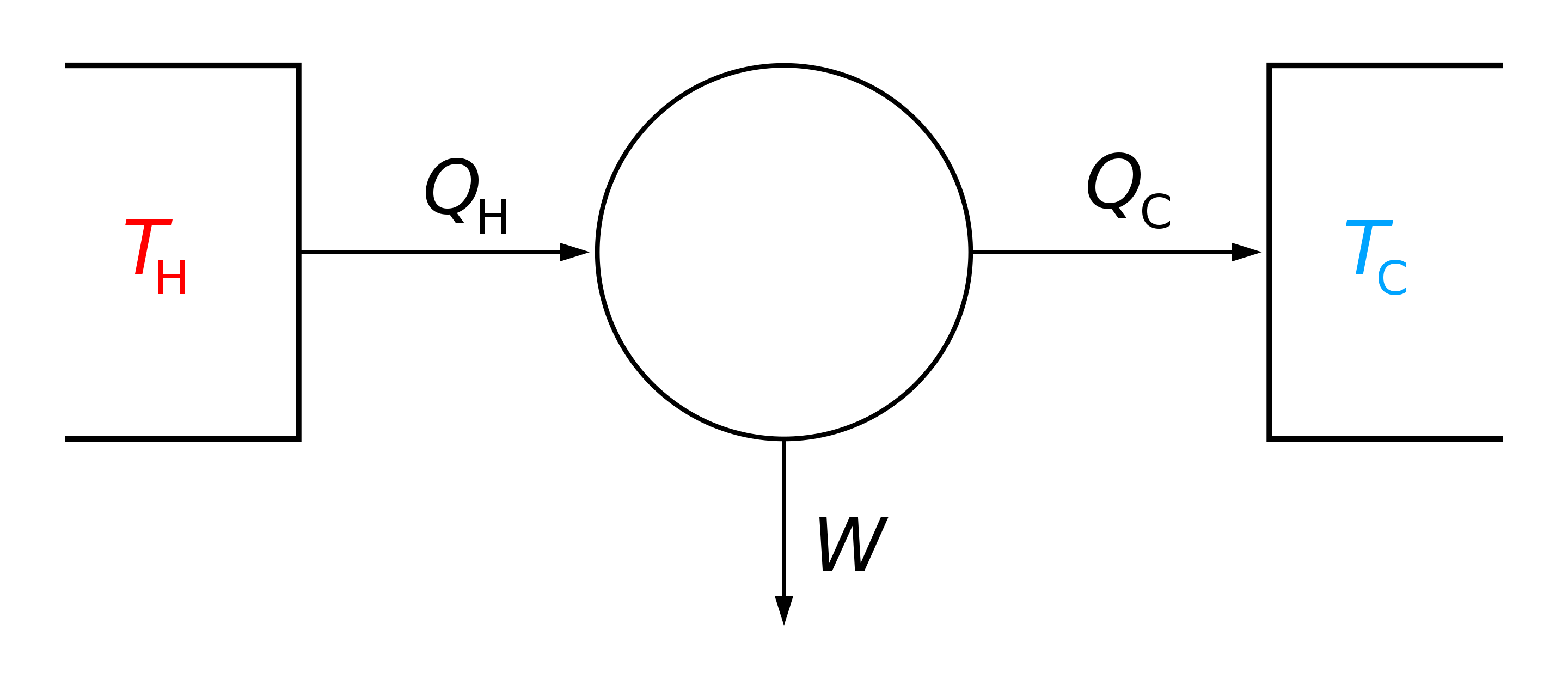
Heat -> Mechanical energy (work)
Source: Wikipedia
Laws of thermodynamics
Zeroth law
“If two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.”First law
“In a process without transfer of matter, the change in internal energy, \(\Delta U\), of a thermodynamic system is equal to the energy gained as heat, \(Q\), less the thermodynamic work, \(W\), done by the system on its surroundings.”Second law
“Heat does not spontaneously flow from a colder body to a hotter body.”Third law
“As the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, all processes cease and the entropy of the system approaches a minimum value.”
Read more: Wikipedia
Three efficiencies
- 1st law: actual, thermal efficiency;
\(\eta_1 =\frac{W_{net}}{Q_{in}}=\frac{Q_{high}-Q_{low}}{Q_{high}}=1-\frac{Q_{low}}{Q_{high}}\) - Carnot: maximum possible efficiency;
\(\eta_c =\frac{W_{net}}{Q_{high}}=\frac{T_{high}-T_{low}}{T_{high}}=1-\frac{T_{low}}{T_{high}}\) (Kelvin)
- 2nd law: comparing 1st and Carnot;
\(\eta_2 =\frac{\eta_1}{\eta_c}\)
Read more: Sadi Carnot
How steam coal plants work
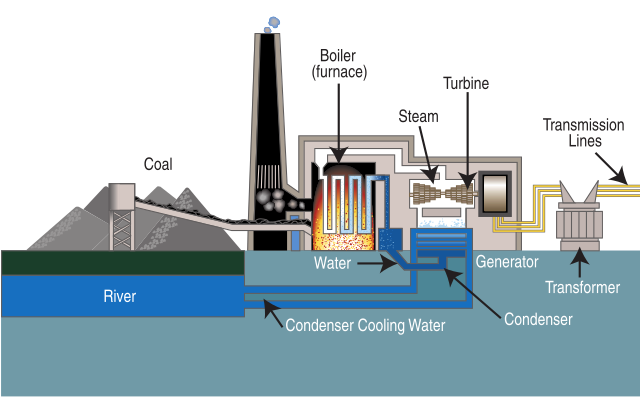
Source: Wikipedia
Brayton cycle vs. Rankine cycle
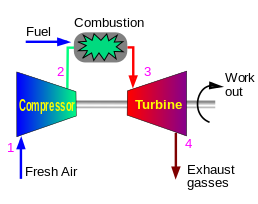
Jet engine, gas turbine
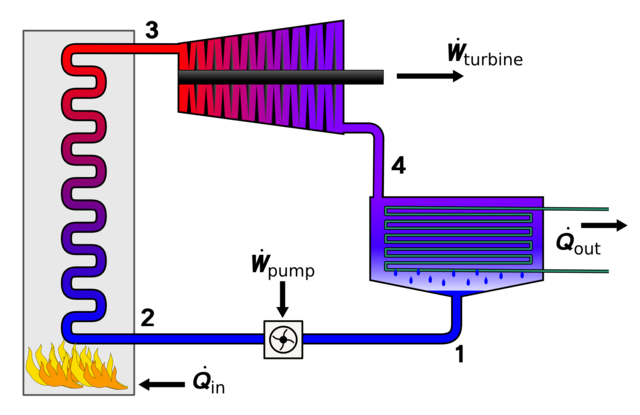
Steam engine, steam turbine
Read more: Wikipedia Brayton cycle and Rankine cycle
Largest coal plant in the U.S.
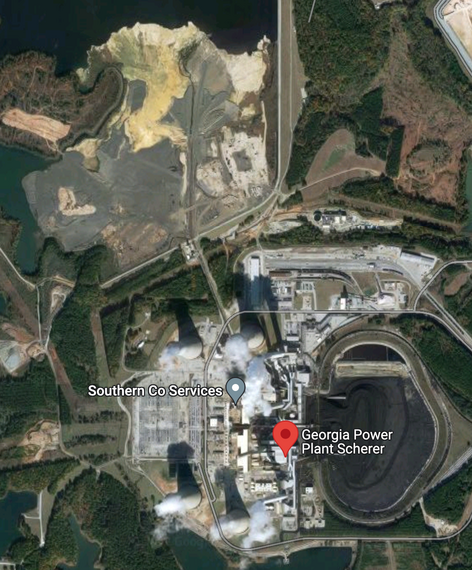
Georgia Power plant Scherer (3,720 MW)
Can you identify the components
- Coal storage
- Generating unit
- Cooling stack
- Bottom ash landfill
- Sub-station
- Transimission lines
- Waste/pollution management
Source: Google Map, read more: Nowhere to hide
Combined cycle
Read more: Tennessee Valley Authority
Wind

\(P=\frac{1}{2}\rho \pi r^2 v^3\)
Where,
\(\rho\) = Density (kg/m3)
\(A\) = Swept Area (m2) = \(\pi r^2\)
\(v\) = Wind Speed (m/s)
\(P\) = Power (W)
Photo by Gang He
Betz’s law: 59.3%
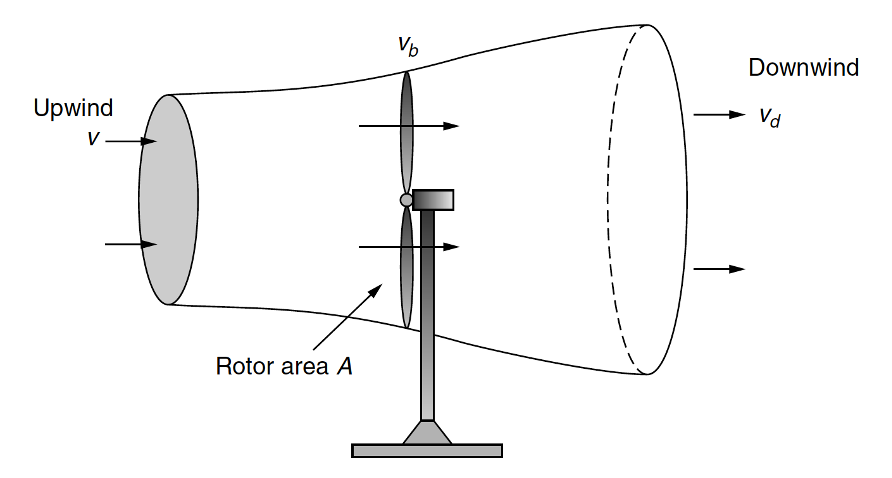
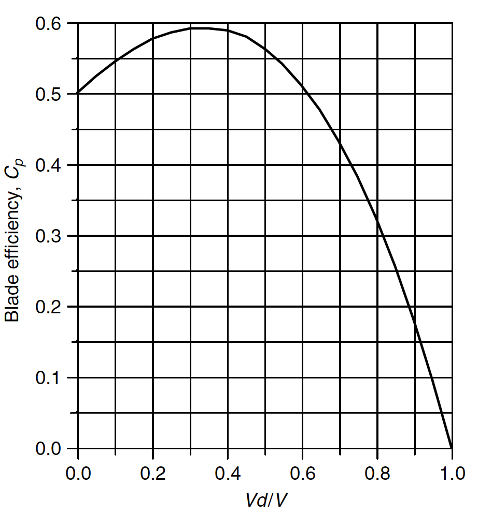
Source: Masters (2013)
Average power
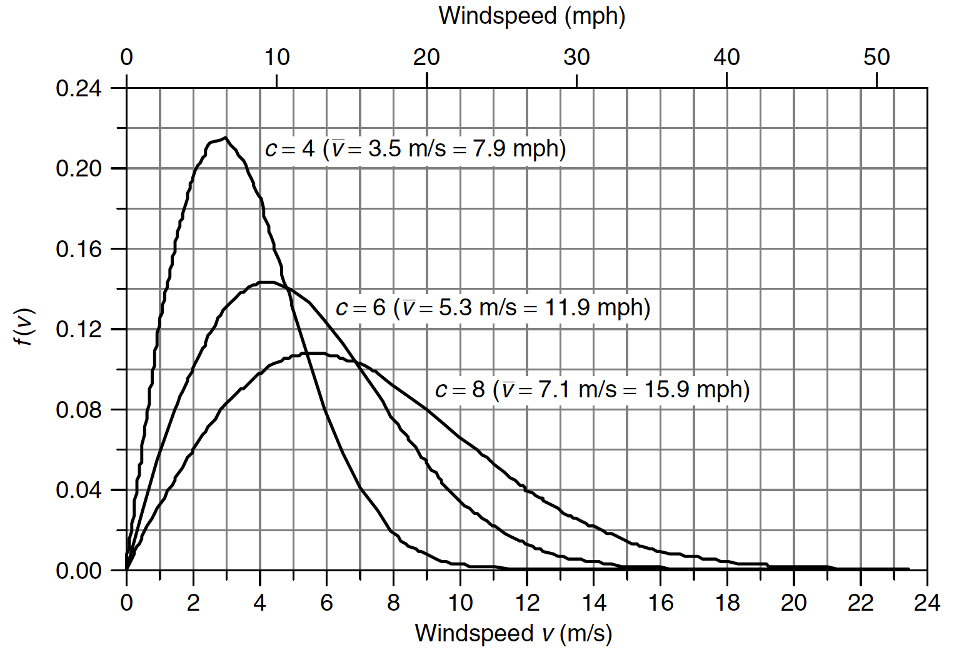
Rayleigh (a special type of Weibull) distribution
\(f(v)=\frac{2v}{c^2}\exp [-(\frac{v}{c})^2]\)
\(\bar{P}=\frac{6}{\pi}\cdot \frac{1}{2}\rho \pi r^2 \bar{v}^3=1.91P\)
Use average power when dealing with average wind speed
Read more: Masters (2013)
Power curve
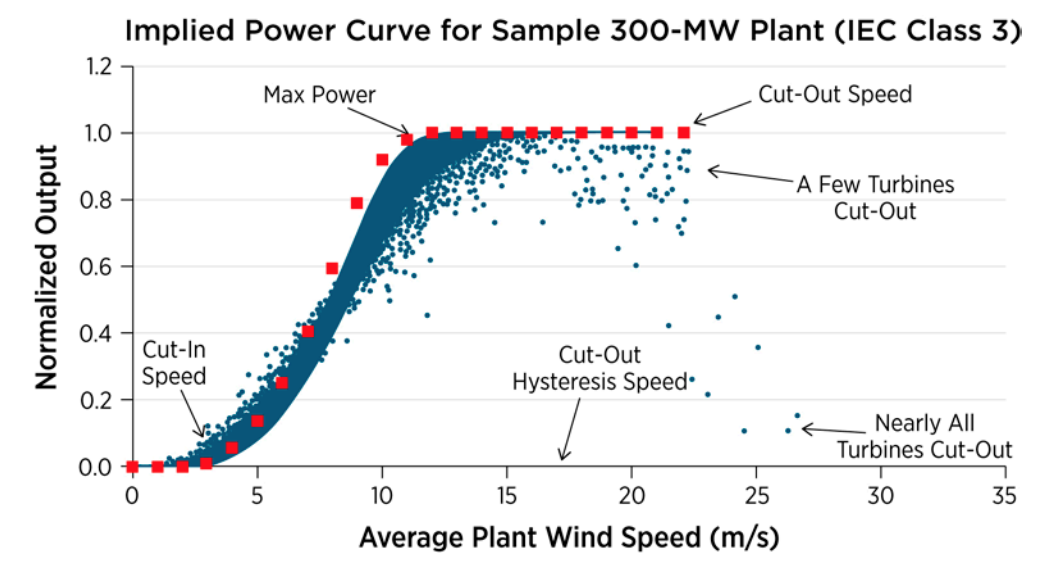
Read more: NREL, Validation of Power Output for the WIND Toolkit
Important corrections
- Temperature: \(\rho = \frac{P\times M.W. \times 10^{-3}}{RT}=\frac{1 atm\times 28.97 g/mol \times 10^{-3}kg/g}{8.2056\times 10^{-5}m^3\cdot atm/(K\cdot mol)\times(273.15+T)K}\)
- Altitude: \(P=P_0 e^{-1.185\times 10^{-4}H}\) (H is elevation in meters)
- Tower height: \(\frac{v}{v_0}=(\frac{H}{H_0})^\alpha\) (is the friction coefficient)
Read more: Masters (2013)
Solar
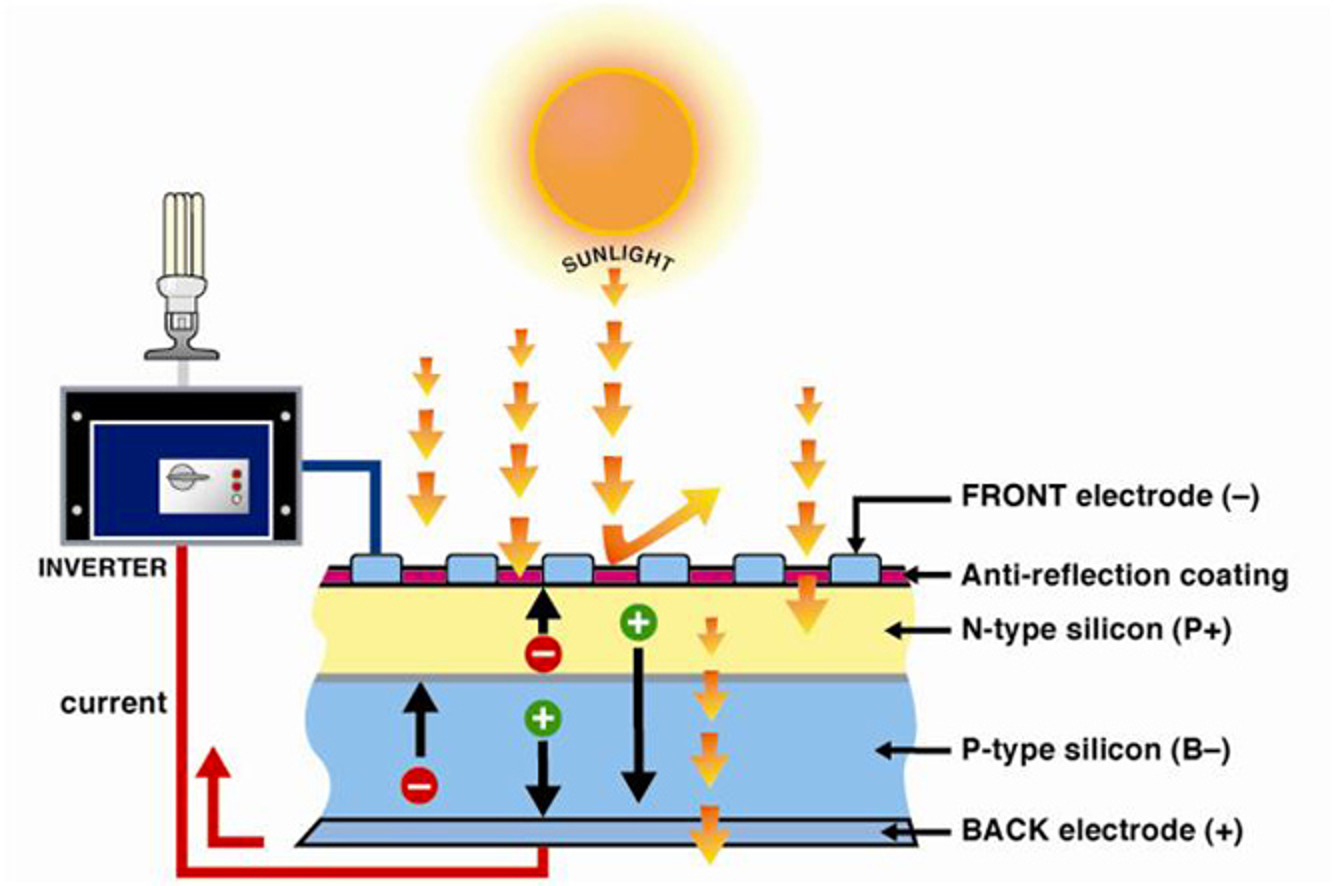
How solar works
Key corrections
- Solar position at any time of day: altitude angle, latitude, zaimuth angle, hour angle
- Radiation: direct beam, diffusion, reflected
- Tracking: fixed, 1-axis, 2-axis
Read more: Masters (2013)
Hydro
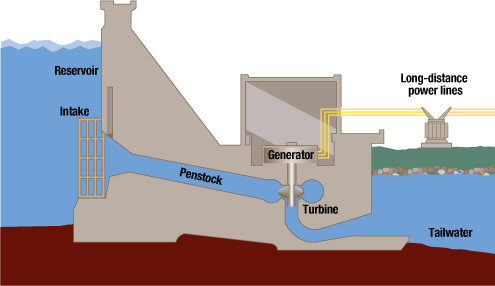
Hydropower
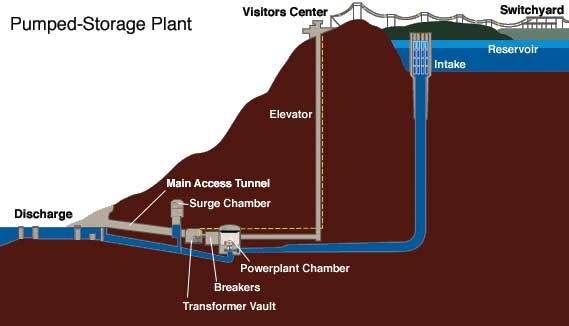
Pumped storage hydropower (PSH)
Source: TVA
Nuclear
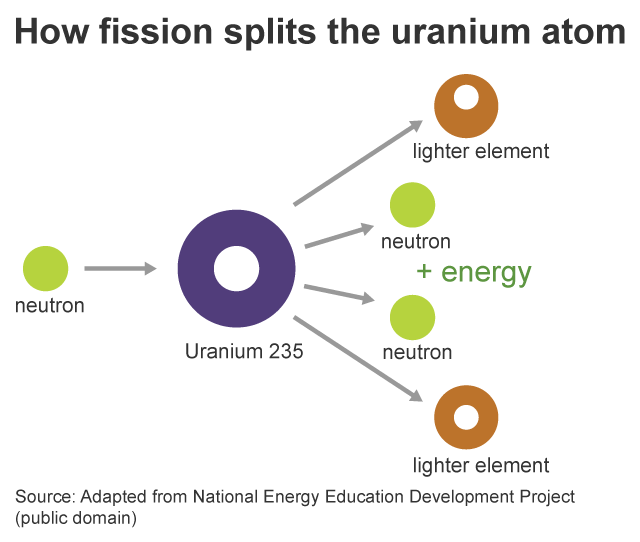
Nuclear fission
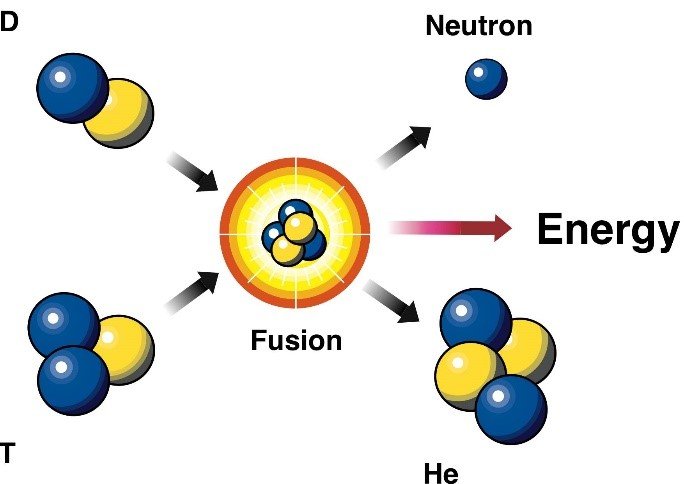
Nuclear fussion
Read more: EIA, Nuclear explained; DOE, Nuclear fusion reactions
Summary
- Theory - learn and understand the physics of energy technologies:
- thermaldynamics (fossil)
- kinematics (wind)
- light and semiconductor (solar)
- gravity (hydro, tidal)
- atomic (nuclear)
- thermaldynamics (fossil)
- Practice - learn all kinds of corrections based on real-world situation
- The physics doesn’t change, corrections help us to do better jobs in simulation and projections